Sidebar
Table of Contents
Logo
Logo is the best and simplest way to start real programming.
- Text based ... start with a blank page
- fun

Traffic Light Check
- Click the green button on each page if you understand
- Click Amber if you are not sure and would like to come back to check
- Click Red if you are stuck The colours will be saved locally. Only on the machine you are using now.
Note for Teachers - Navigation is roughly organised by technique (repeat/subs/abstraction) rather than outcome (SQU, TRI, PENT, CIRC HOUSE, STREET, FOREST) but this rule has been broken.
Getting Started
Open the link below (right click > open in a new browser tab so you can switch back and forth). This site is an Online Logo Interpreter
Here is the link
Remember to keep this window open. You can always open it from this page if you accidently close it.
type the following in the box at the bottom
forward 100
Click Run Then try
right 90
Don't forget to click run
Hint
You can use the short commands fd 100 and rt 90
Task: draw a square
Then try a hexagon and a triangle
Traffic Light Checkpoint
- I am confident in drawing different shapes
Additional resources
- Wikipedia Logo Programming
- Javascript turtle Alternative online Turtle Logo for primary school but too simple eg. you can't use brackets
- Turtle academy A similar approach to the one used here. But much more text.
- Logo to download (not usually necessary unless you are travelling)
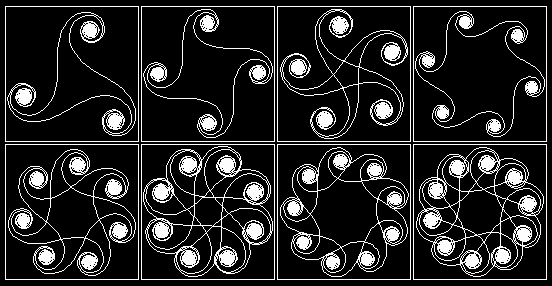
Repeat
It gets boring typing all these commands. Using repeat is quicker. Try this command
repeat 4 [fd 100 rt 90]
Hint:
These are square brackets not curly ones!
Task: draw a pentagon
Then an octagon, decagon (What?), a 10 sided shape, then finish with a circle
Traffic Light Check
- I have done the task and understand it
Sub Routines
Which is easier to understand and type?
repeat 4 [fd 100 rt 90]
or
squ
We are going to teach the computer how to SQU. Using the following code
to SQU
repeat 4 [fd 100 rt 90]
end
- We need a bit more space so open the command window using the black arrow HELP!!
- Enter your code (from above)
- Click Run
- Click on Library (top right) to check that your code has been saved.
- Then to use the SQU command simply type SQU underneath
- The command
clearscreenmight be useful
Task:
- Create a sub for TRI (a triangle)
- Create at least 2 subs for other shapes we have made PENT, HEX, CIRC etc
Theory
When programming it's good name different bits of code.
These different bits of code are called sub routines (we could also say: procedure, a function, a method or just a routine).
Looking at it the other way around we could say that we are going to give a name to the repeat 4 [fd 100 rt 90]
code that we have been using, to make it easier to remember and use.
Traffic Light Checkpoint
- I know HOW to use a subroutine
- I know WHY I am creating a subroutine
Abstraction
Now we have named some sub routines we can combine them into new things. It allows us to abstract (hide) the detail. Programmers also call this black boxing or deconstruction. This is one of the most important skill that programmers have: computational thinking.
Task 1: Create a House using SQU and TRI

HINT (don't use it unless you Reeelly need it!)
Task 2: (Harder) Create a street

Traffic Light Checkpoint
- I have done house and street
- I know that to find the problems in my code I have to 'debug' it (work like a detective)
- I know that programs are split into pieces which are combined together and this is called abstraction
See Also
ARC Challenges
Can you work out how to do the following?
Use the code
To ARC
repeat 90 [fd 1 rt 1]
END
1. Flower
Start with the head first

2. Bird
Can you create a single bird like the ones used in this Flock picture (We will do the whole flock later)

Variables
We can use variables to vary the size of the square

Task: Use your own variables to change the size of shapes (eg. HEX, TRI, SQU)
Traffic Light Checkpoint
- I have done the Task on 2 or more shapes. AND I understand why variables are useful
- I have only done square. Why are we doing this?
- I don't understand this
Extra Challange: Use variables in Subroutines like HOUSE that uses TRI and SQU (this is more complicated that you might think)
Random Variables
Randomness occurs in nature. Use a random variable is a powerful way for you to easily create a natural effect.
random 16will produce a random variable between 0 and 16
for example random colour using the set pen colour command
setpc 16where the number is one of 16 predefined colours
Random Challanges



Checkpoint
- I have used a random variable creatively to obtain a natural effect
Creativity: Logo Art
The best thing about Logo is having fun and doing something that interests you. This way you are sure to be creative.
What do you want to do today?
This image is created in Logo. You can buy a print of it to put on your wall. You can buy a book of images like this which includes the code used to generate it.
- turtleart.org
- Turtle Art Software [Download Page](http://llk.(/media.mit.edu/courses/software/turtleart/)
- online manual
Task: Produce your own piece of art
See if you can get it printed in colour
Traffic Light Checkpoint
- Green: I produced a jpg and sent it to my teacher
- Amber I'm working on this
- Red : I need help
Power of: 15 Word Logo Challanges
Lots of inspiration here to use tiny amounts of code (15 words max) to produce a big effect
Traffic Light Checkpoint
- I tried some of the 15-word examples
- I changed some of the variables to see what effect they had
Recursion
Recursion is an extremely powerful programming technique. It is a loop that 'calls' itself.. a bit like a snake eating its tail. If you don't tell in when to stop it can crash your computer - so it can be dangerous
Recursion is used to create fractals 
It is useful for searching a file system. It goes down from the root into each and every branch (folder) of the system. It is also used by nature to create things like trees. You can see the tree and fern in the examples on Calormen (Josh Bell's) Logo Interpreter


Here is TEF's "Papert Logo Online" with code for the Koch Snowflake
Quote
"The power of recursion evidently lies in the possibility of defining an infinite set of
objects by a finite statement. In the same manner, an infinite number of computations
can be described by a finite recursive program, even if this program contains no explicit
repetitions.
Wirth, Niklaus (1976). Algorithms + Data Structures
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Recursion_(computer_science)#cite_note-3)
See Also
- Wikipedia Koch Snowflake
- Wikipedia Fractal
- [Cargo Bot ](
) - Ipad Game (now free). Great for learning recursion without even knowing it!
- Ipad Game (now free). Great for learning recursion without even knowing it!
Challange/Task
- program the koch snowflake in the Calormen Logo Interpreter
Traffic Light Checkpoint
This is a complex task which will be beyond the reach of most students.. but have a go! Most important is to UNDERSTAND
- Green: I completed the task and understand it
- Amber: I am working on the task
- Red : I need help
- Blank: I'll pass on this one
3D Logo: Elica
Elica is a powerful and modern logo that can produce 3D and moving images.
See Also:
- Elica geometry Video (Youtube)
- Official Elica Site with download link. The demos are great too.
Traffic Light Checkpoint
I have watched at least 2 videos
Teachers Notes
- Environment
- Drawing (younger)=> puzzles: golf, maze see app notes
- Repeating / looping => patterns
- colour here?
- Subs
- House, Street
- Black Boxing(abstraction, computational thinking)
- Random Colour
- Variables
- Creativity =>Art,
- Power of: 15-word challanges
- ??Branching if
- ??Swarming - multi agent Logo
- recursion =>tree koch
- 3D logo =>Elica
Also recursive

???